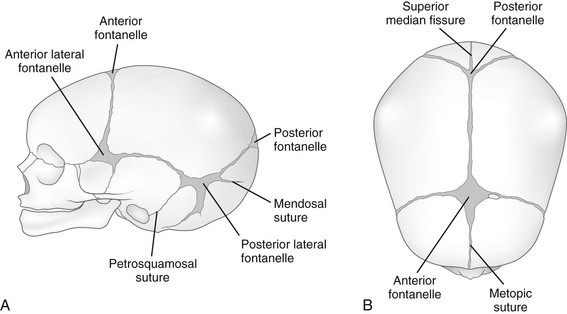
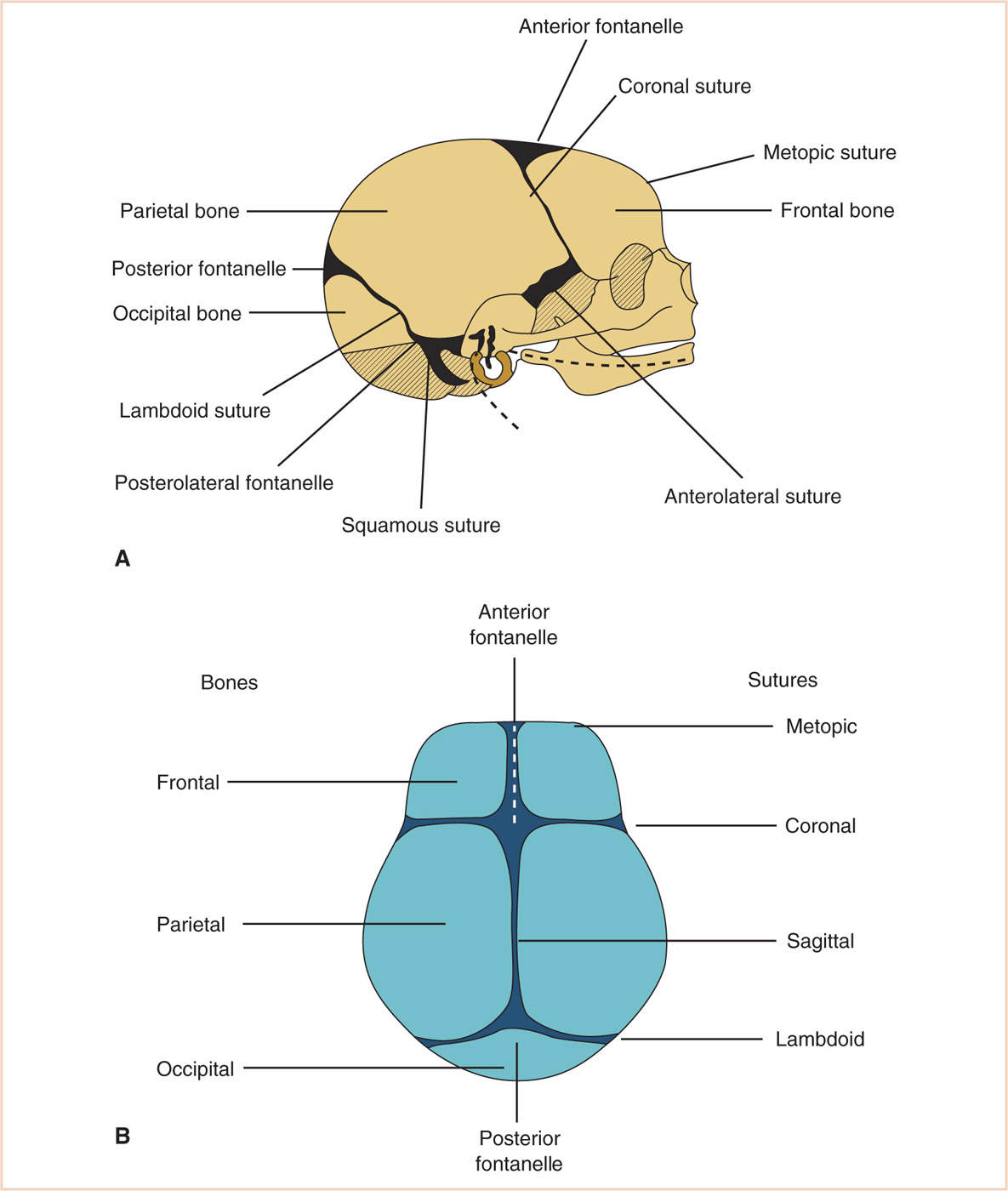
Fontanelles Of Juvenile Skull

Bibliography developmental juvenile osteology 10 1016 b978 012624000 9 50016 2 473 559 2000.
Fontanelles of juvenile skull. A significant difference is the bones of the infant skull are soft and haven t fused yet. Huge collection amazing choice 100 million high quality affordable rf and rm images. Four methods can be used to estimate juvenile age.
No need to register buy now. Auliscomys loxodontomys mareso mys hershkovitz 1962. With advancing age the skull gradually grows and differentiates until late in childhood when all of the essential characteristics of the adult skull have developed figs.
One of the methods is the fusion of the primary ossification centers in the cranium. Fontanelles are membranous areas that have not yet ossified in the developing cranial vault of neonatal and juvenile animals. The rates of this fusion are known.
In the fourth skull there is no appre ciable gap but the bones are unfused in four places. Boggs the genetic aspects of facial abnormalities advances in human genetics 8 10 1007 978 1 4615 8267 0 235 346 1977. The developing skull of newborn and juvenile animals.
150112 had a fenestra 2 8 anteroposterior ly by 3 4 mm. Fontanelles allow for rapid stretching and deformation of the cranium as the brain expands faster than the surrounding bone can grow. The size and shape of the infant skull differs from that of the adult skull.
They permit some movement between the bones so that the developing skull is partially compressible and can slightly change shape. Find the perfect fontanelles stock photo. These membranous areas are called fontanels.